Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
VUMC IT Guide to Working RemotelyVUMC information about communication and collaboration tools
Department Facilities and Resources
Getting Started at Vanderbilt Biostatistics (IT Information)
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Zoom Notes
- Backup procedures
- Data privacy note
- How to map (or mount) a network share
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Virtual Private Network (VPN)
- Dealing with multiple email accounts
- Working with "big data" in R
- How does a new employee get information about getting started in Biostatistics?
- Where can I get information about cyber security?
- How do I share data with a statistician
- Review quarantined email
- Where can I find information about Vanderbilt's high performance compute cluster (ACCRE)?
- How do I get a Shiny app hosted?
- How do I deploy a Shiny app?
- Automount windows share in Ubuntu
- How to operate the Garden Room audiovisual system
- How do I operate the projectors in the 2525 conference room and classroom?
- What are the network addresses (hostnames) for the department's printers?
- How to install printers
- How do I "de-identify" a data set to remove private information?
- Where are "How To" Pages on the Biostatistics Wiki?
- What are some Stata learning resources that you recommend?
- Where can I get some help with R?
- Where can I find "how to" help?
- Where can I get some programming tips?
- How do I run my R program as a batch job?
- How do I make the wiki edit box bigger?
- Wiki topic naming advice
- Remote Access
- LaTex Links and Notes
- How should I organize my directories?
Zoom Notes
Procedures for using ZoomZoom Backgrounds
Backup procedures
For systems that are not backed up by the department, cloud storage can be used. VUMC IT recommends and supports OneDrive/SharePoint.
Workstations supported by the Biostatistics IT staff at 2525 West End Ave are backed up in different ways depending on the type of system. Contact one of the IT team members or email biostat-it@list.vumc.org if you need assistance restoring a file.Windows and Macintosh workstations, Laptops
These systems are not backed up by the department. Windows users can protect important files from loss by using cloud storage. See https://www.vumc.org/it/communicate-and-collaborate. The department also provides network attached storage (NAS) that may be appropriate in some situations. Contact the Biostatistics IT Staff at biostat-it@list.vumc.org with questions.Linux workstations
Linux workstations are backed up daily. Once a day, each user's /home directory is saved to a backup staging server. The files on the staging server are subsequently copied to tape. This is not a permanent archive. We can usually recover a file from up to 3 month ago, but not earlier. The backup tapes are reused and the older backups get overwritten. Linux users may contact the IT staff for assistance recovering files.Data privacy note
Certain kinds of information should be kept private. It is the responsibility of those of us who deal with this information to understand which items should be protected and the tools we can use to do so. See Department of Biostatistics Data Security Policy for an overview of what data should be protected and the tools and policies related to that. See https://www.vumc.org/enterprisecybersecurity/welcome. This is the VUMC Enterprise Cybersecurity home page. Contact a member of the IT staff at biostat-it@list.vumc.org if you have any questions.How to map (or mount) a network share
Let's assume we want to map (or mount) a network share that is being served by a Windows or other SMB server. Lets call the server "i10file.vumc.org" and the share "biostatistics/sharename". The full share name would be "\\i10file.vumc.org\biostatistics\sharename" or "//i10file.vumc.org/biostatistics/sharename" depending on the type of system we are connecting from.
Also assume that your VUMCid is "VUMCid" or "sharename" is the name of the share you are wishing to map or mount.
If you are off campus or connected using the VUMCguest wifi network you will need to make a VPN connection first.
Windows
Map a network drive in Windows 10 (from Microsoft)- Open the file manager
- Right click on "Computer" or "This PC" and select "Map network drive..."
- In the Map Network Drive window that comes up, select an available drive letter. Enter \\i10file.vumc.org\biostatistics\sharename in the "Folder" box.
- If you are using a computer that is logged on the Vanderbilt domain, click Finish and you are done.
- Otherwise, check the box beside "Connect using different credentials" and click the Finish button.
- In the User name box enter "vanderbilt\VUMCid" and enter you epassword in the Password box. Set the "Remember my credentials" check box if you like.
- Click OK. That should be it.
Macintosh
- Open the Finder
- Click on the Go menu and select Connect to Server
- For Server Address enter (for example) smb://i10file.vumc.org/biostatistics/sharename and click the + button
- Click the Connect button
- When prompted enter vanderbilt\VUMCid for the username and your epassword for the password (where "VUMCid" is your VUMCid).
- Select the Remember this password box
- Click the Connect button
Once the share is mounted, the mount point will be /Volumes/sharename.
Linux (credit: https://www.computerhope.com/issues/ch001636.htm)
Access a Windows shared folder from Linux, using NautilusMany Linux distributions, especially those that use the GNOME desktop environment, use the Nautilus file manager. If this is what you're using, you can follow these steps to access your Windows shared folder:
- Open Nautilus.
- From the File menu, select Connect to Server...
- In the Service type: drop-down box, choose Windows share.
- In the Server: field, enter the name of your computer.
- Click Connect.
Alternatively, in the Nautilus address bar, you can type smb://ComputerName/ShareName and press Enter. For instance, when you created your Windows Share, if the share name was listed as:
\\i10file.vumc.org\biostatistics\ShareFolderName
Type
smb://i10file.vumc.org/biostatistics/ShareFolderName
and press Enter. Note the smb: at the beginning, and that on Linux you should use forward slashes instead of backslashes.
Once the share is mounted, the mount point will be /run/user/username_or_userid/gvfs. For ease of access a link can be created to the mount point.ln -s /run/user/<username_or_userid>/gvfs ~/.gvfsAccess a Windows shared folder from Linux, using the command line
You can also access your Windows share from the Linux command line using the smbclient program.
- Open a terminal.
- Type smbclient at the command prompt.
- If you receive a "Usage:" message, this means smbclient is installed, and you can skip to the next step. If the command is not found, however, you need to install smbclient. Follow these steps to install it.
sudo apt-get install smbclient command.
- With smbclient installed, you can connect to your Windows share using the command
smbclient //ComputerName/ShareName -U Username. For instance, if your VUMCid is doejoh, and your Windows share network name is//i10file.vumc.org/biostatistics/ShareFolderName, use the commandsmbclient //i10file.vumc.org/biostatistics/ShareFolderName -U doejoh. Notice that the Linux command uses forward slashes instead of backslashes).
- Enter your password.
- Once authenticated, you are placed at an smb: \> prompt.
- Here, you can use the ls command to list files.
- Use the command get filename.ext to transfer a file named filename.ext from your Windows share to your Linux machine, for example.
- Type help for a listing of further commands.
- Type quit or exit to return to the command prompt.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
See MFA at VUMC.Virtual Private Network (VPN)
See Virtual Private Network - Remote Access. The instructions are complete and detailed, but need to be read carefully if the process is to go smoothly.Dealing with multiple email accounts
- How to add a second email to Outlook (from a workstation) (VUMC instructions)
- How to add a second email to Outlook (from a mobile device) (VUMC instructions))
How to add an email account in the Macintosh email application
- Open the Apple email application
- Click on the "Mail" menu item
- Click "Add account..."
- Select "Exchange" and click Continue
- Enter your email address (VU or VUMC as appropriate) and corresponding epassword
- Click the Sign in button
- Click Done on the next window that appears.
If I have 2 email accounts, how do I redirect email to the correct account?
NOTE: Automatically forwarding email into or out of the VUMC email system is prohibited by VUMC policy.An option is to put an autoresponder on your non-primary email account. The autoresponder would reply to any email coming into that account and inform the sender that you dont want to receive email at that address. It should also mention your preferred address.
Working with "big data" in R
Here are links to some resources- https://www.rstudio.com/resources/webinars/working-with-big-data-in-r/
- http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S221457961630065X
- http://www.datasciencecentral.com/profiles/blogs/r-for-big-data-in-one-picture
How does a new employee get information about getting started in Biostatistics?
Our wiki has a "Getting Started at Vanderbilt Biostatistics" topic. This topic is a collection of some of what one needs to know to get started at Biostatistics. The focus mainly on Information Technology and related subjects.Where can I get information about cyber security?
See the Data Security section of Getting Started at Vanderbilt Biostatistics topic.How do I share data with a statistician
- Tidy Data by Hadley Wickham (PDF)
- How to Share Data with a Statistician (blog article)
- Spreadsheet from Heaven and Spreadsheet from Hell. These are example spreadsheets from Dan Byrne that demonstrate the proper way and the improper way of entering data for a clinical research project.
Review quarantined email
VUMC uses a service that scans all email for spam and malware. If an email is detected to be spam or containing malware, it is quarantined and not delivered to your inbox. There are occasional false positives. If you wish to review your quarantined email follow these steps:- In a web browser, navigate to https://protection.office.com
- Log on with your VUMC credentials
- Click on "Threat Management" and then "Review"
- Click on the Quarantine link. A shortcut to this is https://protection.office.com/#/quarantine
- Review your messages marked as spam
Where can I find information about Vanderbilt's high performance compute cluster (ACCRE)?
How do I get a Shiny app hosted?
How do I deploy a Shiny app?
Note: The Shiny server referenced here is not intended for critical applications or for apps that require guaranteed uptime or quick recovery from hardware failure. If you have those requirements send an email to biostat-it@list.vumc.org with details of your needs. We have set up a Shiny server on our statcomp2 server. See for example https://statcomp2.app.vumc.org/VisualPruner/Please note: We are using the open source, community supported version of Shiny Server that does not have some of the features of the commercial version. One of the missing features in this version is password protection. Please also remember that our shiny server is not appropriate for apps that require guaranteed uptime or quick recovery from hardware failure.
To install your shiny app on the statcomp2 server, do the following:
- Develop your shiny app and get it working on your workstation.
- Ask the Biostatistics IT team for an account on statcomp2.emp.vumc.io if you dont already have one.
- Log on to your statcomp2 account and make a new sub-directory called
/home/VUMCid/ShinyApps/(where VUMCid is your VUMCid) - Make an appropriately named directory in
/home/VUMCid/ShinyApps/. For example, if your app is called "MyApp1" then make a directory/home/VUMCid/ShinyApps/MyApp1. - Copy your Shiny application to this new directory.
- Let us know when you are done at biostat-it@list.vumc.org. A link has to be added. After that your application will be live. Also, let me know what packages your app uses. We might need add them.
Automount windows share in Ubuntu
See http://stackoverflow.com/questions/33566227/automount-windows-share-in-ubuntu-14-04-ltsLets say there is a share being served from a Windows computer that we need to use regularly. We'd like to mount that share on our Linux computer.
In the notes below- $SERVER is the name of the server
- $SHARE is the the name of the share to be mounted
- $VUMCid is the user's VUnet ID
- $EPASSWORD is the user's ePassword
- $MOUNTPOINT is a directory serving as the local mount point. This is typically named the same as the share but can be any directory that the user can write to. This directory must be empty.
mkdir /home/$VUMCid/$MOUNTPOINTAdd this line at the end of the
/etc/fstab file
//$SERVER/$SHARE /home/$VUMCid/$MOUNTPOINT cifs credentials=/home/$VUMCid/.smbcredentials,uid=$VUMCid,domain=vanderbilt,iocharset=utf8,_netdev,sec=ntlm 0 0Create a file called
/home/$VUMCid/.smbcredentials. Put these lines in that file.
username=$VUMCid password=$EPASSWORD domain=vanderbiltProtect
.smbcredentials (it contains a password!).
chmod 600 /home/$VUMCid/.smbcredentialsMount the share
sudo mount -a
How to operate the Garden Room audiovisual system
How do I operate the projectors in the 2525 conference room and classroom?
To turn the system on, press the VGA or HDMI button as appropriate.- Use the HDMI button for the conference room Linux computer, Apple TV device, or anything else connected to the podium switch box. This could be a speaker provided laptop.
- Use the VGA button for anything connected to the black extension cable (most likely a speaker provided laptop).
It will take a minute or two for the system to lower the screen, turn on the projector, and warm up. Please press the button only once.
To turn the system off, press the DISPLAY OFF button. It will take a minute or so for the system to raise the screen and shut down. The DISPLAY ON and DISPLAY OFF lights will flash during the shutdown process. Please press the button only once. Please turn the system off when you are finished. Contact Dale or one of the IT Team if you have problems. There is no need to press any of the other buttons.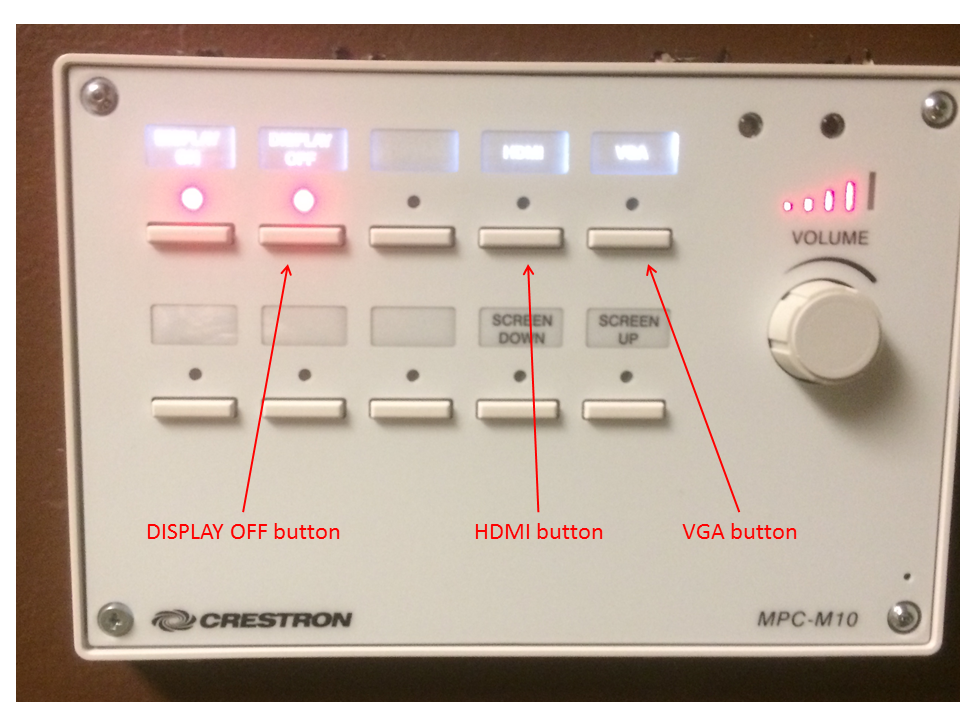
What are the network addresses (hostnames) for the department's printers?
If you want to install your own printer drivers you will need to know the network address of the printer you wish to install. Most installation tools will attempt to find all the printers on the network and let you pick one. This rarely works because there are so many printers around and sometimes the printer you want is not found. It is better to specify explicitly the printer in question. All installation processes I have seen provide an option to specify the printer web address directly.The type of printer can be also be found there. You'll need to know that when installing the printer. You'll also need to know the printer type if you have to download a driver from the manufacturer.
The procedure for installing these printers on the Linux computers is on the workstation setup wiki page.How to install printers
You will need the printer host names: https://biostat.app.vumc.org/wiki/Main/PrinterHostnames...on the Linux workstations
See the workstation printer set up instructions...on Windows 10 computers
See Windows 10 instructions for installing printers (pdf)...on Macintosh computers
See Macintosh instructions for installing printers (pdf)How do I "de-identify" a data set to remove private information?
- See the Data De-identification Checklist wiki topic.
- Notes on Data Protection from a European perspective
Where are "How To" Pages on the Biostatistics Wiki?
How To PagesWhat are some Stata learning resources that you recommend?
Each of these will have some information that is specific to the originating institution. From Princetonhttp://www.princeton.edu/~otorres/Stata/
http://dss.princeton.edu/training/StataTutorial.pdf UCLA Academic Technology Services
http://www.ats.ucla.edu/stat/stata/
http://www.ats.ucla.edu/stat/stata/sk/default.htm Economic and Social Data Service, UK
http://www.esds.ac.uk/government/docs/documents/StartingStata9.pdf Institute of Economic Education, WWU Münster
http://www.wiwi.uni-muenster.de/ioeb/Downloads/Forschen/Pfaff/Introduction_to_Stata_with_50+_Basic_Commands.pdf
Where can I get some help with R?
See Frank's R and S-Plus Packages, Functions, and Documentation. Of interest to new R users is Terri Scott's "An Introduction to the Fundamentals & Functionality of the R Programming Language" and other lecture notes that can be found on her page. Also of interest to R users coming from SAS or SPSS is http://RforSASandSPSSusers.com R for SAS & SPSS Users by Robert Muenchen.Where can I find "how to" help?
There are a lot of useful how to pages on our site. See How To Pages on the Biostatistics WikiWhere can I get some programming tips?
"I am a statistician, not a programmer." How often have you heard this? See Programming Tips For Statisticians for programming hint and tips.How do I run my R program as a batch job?
The problem: If one runs a program as an interactive job (i.e. connected with a terminal session) then the job will be terminated if the interactive session gets disconnected. The interactive session will most certainly get disconnected if it sits idle without any keyboard input or video output for a while. This is a feature of the Vanderbilt network that we cannot change.The best way to execute long running jobs is to run them as batch jobs. When running as a batch job, the process is not dependent on the existence of a terminal session. One can launch the job and log out and it will continue to run.
Let's say we have a R program called "helloworld.R".
You can execute an R script from the command line by using a command like this:
$ Rscript helloworld.ror
$ Rscript helloworld.r > helloworld.RoutThis will execute the R commands that are stored in the file helloworld.R and write the output to a file helloworld.Rout.
But if it is a long running job then your terminal session might get disconnected before the program is complete.
One of the following techniques will allow you to run the job without the job being dependent on a terminal session.
Then use one of these techniques:
- Use the "nohup" command to run the script, e.g.:
$ nohup Rscript helloworld.R > helloworld.Rout &
- use the "at" command to submit the script to a batch queue, e.g.:
$ at now at> Rscript helloworld.R > helloworld.Rout at> ctrl-d $
at now means to run the batch job immediately ("now"), but you can specify any time in the future.
Be sure to read the man pages for nohup (man nohup) and at (man at) for further details.
How do I make the wiki edit box bigger?
The edit box used to create and edit wiki pages is pretty small and the font is too little. How can I make these bigger? To make the edit box bigger, add two lines like these to your personal page:* Set EDITBOXWIDTH = 70 * Set EDITBOXHEIGHT = 25The 70 and 25 can be changed to suit your tastes, but these values seem to work pretty well.
In the Firefox web browser, the font size in the twiki edit box can be changed by going to the Edit menu, clicking on Preferences, then clicking on the Content item. Click on the Advanced button in the Font & Colors section. In the Fonts dialog that appears change the Monospace font size to something a little larger than the default (16 is a pretty good size).
Wiki topic naming advice
Over time several Wiki users have created topics for specific reasons but have assigned generic names to these topics (e.g. JournalClubICUD, MyLearning). There is nothing wrong with this but in some circumstances it can prevent a later user from creating a topic that needs to be fully generic. This is more important now that you can link to a topic with a short name you can publish, such as biostat.mc.vanderbilt.edu/MyTopic . It would be best if we reserved generic names for topics that are for general use that spans multiple groups. You might consider using names such as ProjxJournalClub for Project X's Journal Club.Thanks for your consideration.
Remote Access
- Tools that can be used on a Windows system to access your office Linux workstation or one of the Biostatistics servers:
- WinSCP (see http://winscp.net/eng/index.php) is an open source SCP (Secure CoPy) client for Windows using SSH (Secure SHell). Its main function is safe copying of files between a local and a remote computer.
- putty (see http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/) is a free Telnet and SSH client. It is used for a command line connection to the remote computer.
- Tools that can be used on a Linux system to access your Linux workstation or one of the servers:
- ssh
- scp
Notes from Jeremy's "Working Remotely" seminar
LaTex Links and Notes
- LaTex cheat sheet
- Commands to invoke LaTex and view or print the output:
Linux $ latex test.tex # invokes LaTex, processes test.tex, and writes test.dvi $ kdvi test.dvi # opens test.dvi for viewing and printing Windows (MiKTex) > latex test.tex > yap test.tex
How should I organize my directories?
| I | Attachment | Action | Size | Date | Who | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
1.jpg | manage | 55 K | 23 May 2011 - 15:13 | DalePlummer | |
| |
2.jpg | manage | 33 K | 23 May 2011 - 15:12 | DalePlummer | |
| |
AddCalendar.pdf | manage | 252 K | 03 Feb 2021 - 15:04 | DalePlummer | |
| |
AddPrinterWindows10.pdf | manage | 720 K | 10 Feb 2021 - 14:31 | DalePlummer | |
| |
HP_M651_Windows_Install.docx | manage | 737 K | 16 Jul 2015 - 09:31 | DalePlummer | |
| |
HP_M651_Windows_Install.pdf | manage | 442 K | 16 Jul 2015 - 09:31 | DalePlummer | |
| |
How_to_Install_a_Printer.pdf | manage | 548 K | 21 Jun 2023 - 14:48 | DalePlummer | |
| |
Letterhead2012-bottom.png | manage | 12 K | 26 Nov 2012 - 10:26 | DalePlummer | letter head bottom portion in png format |
| |
Letterhead2012-top.png | manage | 32 K | 26 Nov 2012 - 10:25 | DalePlummer | letter head top portion in png format |
| |
Letterhead2012.doc | manage | 92 K | 26 Nov 2012 - 10:24 | DalePlummer | letter head in microsoft word format |
| |
Letterhead2012.odt | manage | 81 K | 26 Nov 2012 - 11:37 | DalePlummer | letter head in odf document format |
| |
Letterhead2012.pdf | manage | 95 K | 26 Nov 2012 - 10:25 | DalePlummer | letter head in pdf format |
| |
Letterhead2012.png | manage | 69 K | 26 Nov 2012 - 10:25 | DalePlummer | letter head in png format |
| |
Letterhead2014.doc | manage | 92 K | 24 Mar 2014 - 10:34 | DalePlummer | |
| |
Letterhead2014.odt | manage | 45 K | 24 Mar 2014 - 10:40 | DalePlummer | |
| |
Letterhead2014.pdf | manage | 34 K | 24 Mar 2014 - 10:34 | DalePlummer | |
| |
Letterhead2014.png | manage | 29 K | 24 Mar 2014 - 10:47 | DalePlummer | |
| |
garden_room_av.pdf | manage | 101 K | 24 Sep 2015 - 14:57 | DalePlummer | |
| |
mac_xerox_printer_installation_1.pdf | manage | 3 MB | 16 Nov 2012 - 11:50 | DalePlummer | |
| |
photo.png | manage | 1 MB | 27 Feb 2014 - 15:34 | DalePlummer | |
| |
virusthreatsettings.pdf | manage | 1 MB | 22 Dec 2020 - 15:58 | DalePlummer |
 Copyright &© 2013-2022 by the contributing authors. All material on this collaboration platform is the property of the contributing authors.
Copyright &© 2013-2022 by the contributing authors. All material on this collaboration platform is the property of the contributing authors. Ideas, requests, problems regarding Vanderbilt Biostatistics Wiki? Send feedback